假设有一个能装入总体积为T的背包和n件体积分别为w1,w2,…wn的物品,能否从n件物品中挑选若干件恰好装背包,即使w1+w2+…+wm=T,要求找出所有满足上述条件的解。
+例如:当T=10,各件物品的体积{1,8,4,3,5,2}时,可找到下列4组解:
(1,4,3,2)(1,4,5)(8,2)(3,5,2)可利用回溯法的设计思想来解决背包问题。首先,将物品排成一列,然后,顺序选取物品装入背包,若已选取i件物品后未满,则继续选取第i+1件,若该件物品“太大”不能装入,则弃之,继续选取下一件,直至背包装满为。
如果在剩余的物品中找不到合适的物品以填满背包,则说明“刚刚”装入的物品“不合适”,应将它取出“弃之一”,继续再从“它之后”的物品中选取,如此重复,直到求得满足条件的解,或者无解。
+由于回溯求解的规则是“后进先出”,自然要用到“栈”。 +进一步考虑:如果每件物品都有体积和价值,背包又有大小限制,求解背包中存放物品总价值最大的问题解---最优解或近似最优解。
+一个能装入总体积为T的背包和n件体积分别为w1,w2,…wn的物品,能否从n件物品中挑选若干件恰好装背包,即使w1+w2+…+wm=T
相当于取一个向量 = ,其中 ,使得 ,求所有满足条件的 。
+使用暴力 dfs 搜索,搜索每一件物品的选择情况,符合条件时输出。
使用 sum+w[k]<=T 进行剪枝,提高运行速度
总情况数为 ,时间复杂度为 。
+#include <stdio.h>
+#include <stdlib.h>
+#define MAX_N 100
+
+int T;
+int n;
+int w[MAX_N];
+int x[MAX_N];
+int solution_count = 0;
+
+// dfs函数,t为当前搜索的层数,sum为当前已经选择的物品的体积和,k为当前搜索的物品编号
+void dfs(int t, int sum, int k) {
+ if (sum == T) {
+ solution_count++;
+ if (solution_count > 50)
+ return;
+ // 输出解
+ int *re = malloc(sizeof(int) * k);
+ int j = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
+ if (x[i]) {
+ re[j++] = w[i];
+ }
+ }
+ for (int i = 0; i < j; i++) {
+ printf("%d ", re[i]);
+ }
+ printf("\n");
+ } else if (sum < T && k < n) {
+ // 剪枝,提高运行速度
+ if (sum + w[k] <= T) {
+ // 选第k件物品
+ x[k] = 1;
+ dfs(t + 1, sum + w[k], k + 1);
+ }
+ // 不选第k件物品
+ x[k] = 0;
+ dfs(t + 1, sum, k + 1);
+ }
+}
+
+int main() {
+ freopen("data.in", "r", stdin);
+ // freopen("data.out", "w", stdout);
+ scanf("%d", &T);
+ scanf("%d", &n);
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ scanf("%d", &w[i]);
+ }
+ // 搜索
+ dfs(0, 0, 0);
+ printf("Total Solution Count: %d\n", solution_count);
+ return 0;
+}
+
+10
+6
+1 8 4 3 5 2
+1 4 3 2
+1 4 5
+8 2
+3 5 2
+Total Solution Count: 4
+将题目拓展为背包问题,使用 dp 算法解决
#include <stdio.h>
+#include <stdlib.h>
+
+int T, M, t[105], w[105];
+int dp[1005][1005];
+
+int max(int a, int b) { return a > b ? a : b; }
+
+int main() {
+ freopen("dp.in", "r", stdin);
+ scanf("%d%d", &T, &M);
+ for (int i = 1; i <= M; i++) {
+ scanf("%d%d", &t[i], &w[i]);
+ }
+ dp[0][0] = 0;
+ // dp[i][j]表示前i件物品,体积为j时的最大价值
+ for (int i = 1; i <= M; i++) {
+ for (int j = 1; j <= T; j++) {
+ // 如果第i件物品的体积大于j,那么就不能选第i件物品
+ if (j < t[i])
+ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
+ else
+ // 否则就是选或者不选第i件物品的最大值
+ dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i - 1][j - t[i]] + w[i]);
+ }
+ }
+ printf("%d\n", dp[M][T]);
+ // for(int i=1;i<=M;i++){
+ // for(int j=1;j<=T;j++){
+ // printf("%d ",dp[i][j]);
+ // }
+ // printf("\n");
+ // }
+
+ return 0;
+}
+10 6
+1 1
+8 4
+4 2
+3 2
+5 3
+2 2
+7
+一个农夫带着一只狼、一只羊和一棵白菜,身处河的南岸。他要把这些东西
+全部运到北岸。他面前只有一条小船,船只能容下他和一件物品,另外只有农夫 +才能撑船。如果农夫在场,则狼不能吃羊,羊不能吃白菜,否则狼会吃羊,羊会 +吃白菜,所以农夫不能留下羊和白菜自己离开,也不能留下狼和羊自己离开,而 +狼不吃白菜。请求出农夫将所有的东西运过河的方案。
+求解这个问题的简单方法是一步一步进行试探,每一步搜索所有可能的选择,对前一步合适的选择后再考虑下一步的各种方案。要模拟农夫过河问题,首先需要对问题中的每个角色的位置进行描述。可用4位二进制数顺序分别表示农夫、狼、白菜和羊的位置。用0表在南岸,1表示在北岸。例如,整数5 (0101)表示农
+夫和白菜在南岸,而狼和羊在北岸。
现在问题变成:从初始的状态二进制0000(全部在河的南岸)出发,寻找一种全部由安全状态构成的状态序列,它以二进制1111(全部到达河的北岸)为最终目标。总状态共16种(0000到1111),(或者看成16个顶点的有向图)可采用广度优先或深度优先的搜索策略---得到从0000到1111的安全路径。
以广度优先为例:整数队列---逐层存放下一步可能的安全状态;Visited[16]数组标记该状态是否已访问过,若访问过,则记录前驱状态值---安全路径。
+最终的过河方案应用汉字显示出每一步的两岸状态。
+使用 dfs 搜索,搜索每一步的选择情况,符合条件时输出。
#include <stdio.h>
+#include <stdlib.h>
+
+int state = 0;
+int v[16];
+char labels[4][16] = {"农夫", "狼", "羊", "菜"};
+int re[16];
+int xx[16];
+int k = 0;
+
+void pt(int command, int state) {
+ int *f = malloc(sizeof(int) * 4);
+ for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
+ // 计算每一位的值
+ f[i] = (state >> i) & 1;
+ }
+ // 按照命令输出
+ if (command == 0) {
+ printf("农夫自己过河\n");
+ } else if (command == 1) {
+ printf("带 狼 过河\n");
+ } else if (command == 2) {
+ printf("带 羊 过河\n");
+ } else if (command == 3) {
+ printf("带 菜 过河\n");
+ }
+ printf("A > ");
+ for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
+ if (f[i] == 1) {
+ printf("%s ", labels[i]);
+ }
+ }
+ printf("\n");
+ printf("B > ");
+ for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
+ if (f[i] == 0) {
+ printf("%s ", labels[i]);
+ }
+ }
+ printf("\n---------------------\n");
+}
+
+int validate_state(int state) {
+ int *f = malloc(sizeof(int) * 4);
+ for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
+ f[i] = (state >> i) & 1;
+ // printf("%d ", f[i]);
+ }
+ // printf("\n");
+ if (!f[1] ^ f[2] && f[0] ^ f[1]) {
+ return 0;
+ } else if (!f[2] ^ f[3] && f[0] ^ f[2]) {
+ return 0;
+ } else {
+ return 1;
+ }
+}
+
+int trans(int x, int undo) {
+ // 0 表示农夫自己过河
+ // 1 表示带狼过河
+ // 2 表示带羊过河
+ // 3 表示带菜过河
+ int tmp_state = state;
+ if (x == 1) {
+ tmp_state = state ^ 3;
+ } else if (x == 2) {
+ tmp_state = state ^ 5;
+ } else if (x == 3) {
+ tmp_state = state ^ 9;
+ } else {
+ tmp_state = state ^ 1;
+ }
+ // pt(state);
+ // printf("%d > ", x);
+ // pt(tmp_state);
+ if (undo) {
+ v[tmp_state] = 0;
+ state = tmp_state;
+ re[--k] = 0;
+ xx[k] = 0;
+ return 1;
+ }
+ if (validate_state(tmp_state) == 0) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ if (v[tmp_state] == 0) {
+ v[tmp_state] = 1;
+ state = tmp_state;
+ xx[k] = x;
+ re[k++] = state;
+ return 1;
+ }
+ return 0;
+}
+
+void dfs() {
+ // printf(">> %d\n", state);
+ if (state == 15) {
+ for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
+ pt(xx[i], re[i]);
+ }
+ printf("\n");
+ return;
+ }
+ if (trans(0, 0)) {
+ dfs();
+ trans(0, 1);
+ }
+ if (trans(1, 0)) {
+ dfs();
+ trans(1, 1);
+ }
+ if (trans(2, 0)) {
+ dfs();
+ trans(2, 1);
+ }
+ if (trans(3, 0)) {
+ dfs();
+ trans(3, 1);
+ }
+}
+
+int main() {
+ // freopen("data.in", "r", stdin);
+ // freopen("data.out", "w", stdout);
+ v[0] = 1;
+ dfs();
+ return 0;
+}
+无
+带 羊 过河
+A > 农夫 羊
+B > 狼 菜
+---------------------
+农夫自己过河
+A > 羊
+B > 农夫 狼 菜
+---------------------
+带 狼 过河
+A > 农夫 狼 羊
+B > 菜
+---------------------
+带 羊 过河
+A > 狼
+B > 农夫 羊 菜
+---------------------
+带 菜 过河
+A > 农夫 狼 菜
+B > 羊
+---------------------
+农夫自己过河
+A > 狼 菜
+B > 农夫 羊
+---------------------
+带 羊 过河
+A > 农夫 狼 羊 菜
+B >
+---------------------
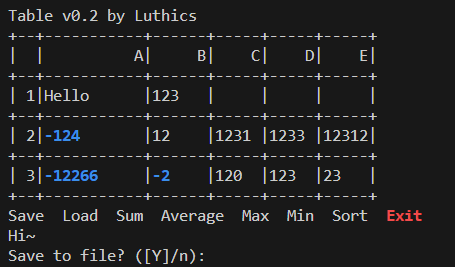
+设计一个支持基本计算统计功能和其它一些表格管理/处理功能的软件,使用 +户可在该软件的支持下,用交互方式进行表格建立、数据输入、数据编辑及其它 +一些表格操作。即类似于简易Execel表格处理软件。
+参考代码中的 main.c,使用 TableInfo 结构体存储表格信息,使用 key.h 存储键盘按键的宏定义,使用 conio.h 实现光标移动,使用 stdlib.h 实现 malloc 函数,使用 string.h 实现 strcpy 函数,使用 stdio.h 实现 printf 函数,使用 math.h 实现 atoi 函数。
大致如下,具体交互功能请运行代码
+
key.h
#define KEY_LEFT_ARROW 0x4B // 左箭头
+#define KEY_UP_ARROW 0x48 // 上箭头
+#define KEY_RIGHT_ARROW 0x4D // 右箭头
+#define KEY_DOWN_ARROW 0x50 // 下箭头
+#define KEY_ENTER 0x0D // 回车
+#define KEY_ESC 0x1B // ESC
+main.c
#include "key.h"
+#include <conio.h>
+#include <stdio.h>
+#include <stdlib.h>
+#include <string.h>
+
+// 一些常量
+#define MAX_COLUMN 20
+#define MAX_ROW 20
+#define MAX_COLUMN_WIDTH 10
+#define MAX_DATA_LENGTH 100
+#define MAX_TICK 200
+#define MAX_MESSAGE_LENGTH 100
+#define FUNCTION_NUM 8
+
+// tick 已废弃
+int tick = 0;
+// 当前光标所在位置
+int current_x = 0;
+int current_y = 0;
+// 当前是否关闭
+int alive = 1;
+// 选择模式是否启用
+int select_mode = 0;
+// 从哪里进入选择模式
+int select_entry = 0;
+// 当前的输入模式
+int input_mode = 0;
+
+// 底部的功能列表
+char functions[FUNCTION_NUM][100] = {"Save", "Load", "Sum", "Average",
+ "Max", "Min", "Sort", "Exit"};
+
+// 当前的消息
+char *message = "Hi~";
+
+// 表格信息
+typedef struct {
+ int current_width;
+ int current_height;
+ int column_width[MAX_COLUMN];
+ char data[MAX_ROW][MAX_COLUMN][MAX_DATA_LENGTH];
+} TableInfo;
+
+// 常用函数
+int max(int a, int b) { return a > b ? a : b; }
+
+int min(int a, int b) { return a < b ? a : b; }
+
+// 计算一个 int 的长度
+int int_length(int num) {
+ if (num == 0)
+ return 1;
+ int length = 0;
+ while (num) {
+ num /= 10;
+ length++;
+ }
+ return length;
+}
+
+// 判断一个字符串是否全是数字
+int is_string_all_number(char *str) {
+ int length = strlen(str);
+ for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
+ if (str[i] < '0' || str[i] > '9') {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ }
+ return 1;
+}
+
+// 判断一行或一列是否全是数字
+int is_index_all_number(TableInfo *table, int type, int index) {
+ if (type == 0) {
+ // 行
+ index = index - 1;
+ for (int i = 0; i < table->current_width; i++) {
+ if (strlen(table->data[index][i]) > 0) {
+ if (!is_string_all_number(table->data[index][i])) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ } else {
+ // 列
+ index = index - 'A';
+ for (int i = 0; i < table->current_height; i++) {
+ if (strlen(table->data[i][index]) > 0) {
+ if (!is_string_all_number(table->data[i][index])) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return 1;
+}
+
+// 交换两列
+void changeTwoColumn(TableInfo *table, int column1, int column2) {
+ // 验证两列是否合法且不等
+ if (column1 == column2 || column1 < 0 || column2 < 0 ||
+ column1 >= table->current_width || column2 >= table->current_width) {
+ return;
+ }
+ char tmp[MAX_DATA_LENGTH];
+ for (int i = 0; i < table->current_height; i++) {
+ strcpy(tmp, table->data[i][column1]);
+ strcpy(table->data[i][column1], table->data[i][column2]);
+ strcpy(table->data[i][column2], tmp);
+ }
+}
+
+// 交换两行
+void changeTwoRow(TableInfo *table, int row1, int row2) {
+ // 验证两行是否合法且不等
+ if (row1 == row2 || row1 < 0 || row2 < 0 || row1 >= table->current_height ||
+ row2 >= table->current_height) {
+ return;
+ }
+ char tmp[MAX_DATA_LENGTH];
+ for (int i = 0; i < table->current_width; i++) {
+ strcpy(tmp, table->data[row1][i]);
+ strcpy(table->data[row1][i], table->data[row2][i]);
+ strcpy(table->data[row2][i], tmp);
+ }
+}
+
+// 自定义支持大小写敏感的字符串比较函数
+int str_cmp(char *str1, char *str2, int case_sensitive) {
+ if (case_sensitive) {
+ return strcmp(str1, str2);
+ } else {
+ char *tmp_str1 = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * strlen(str1));
+ char *tmp_str2 = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * strlen(str2));
+ strcpy(tmp_str1, str1);
+ strcpy(tmp_str2, str2);
+ for (int i = 0; i < strlen(tmp_str1); i++) {
+ if (tmp_str1[i] >= 'A' && tmp_str1[i] <= 'Z') {
+ tmp_str1[i] += 32;
+ }
+ }
+ for (int i = 0; i < strlen(tmp_str2); i++) {
+ if (tmp_str2[i] >= 'A' && tmp_str2[i] <= 'Z') {
+ tmp_str2[i] += 32;
+ }
+ }
+ int result = strcmp(tmp_str1, tmp_str2);
+ free(tmp_str1);
+ free(tmp_str2);
+ return result;
+ }
+}
+
+// 判断一个 index 是否合法
+int check_index_valid(TableInfo *table, char *index) {
+ // 合法的 index 应该是 A1,A23 这样的格式
+ int length = strlen(index);
+ if (length == 0) {
+ return 0;
+ }
+
+ if (index[0] >= 'A' && index[0] <= 'A' + table->current_width - 1) {
+ // 列号合法
+ int row = 0;
+ for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) {
+ if (index[i] < '0' || index[i] > '9') {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ row = row * 10 + index[i] - '0';
+ }
+ if (row >= 1 && row <= table->current_height) {
+ return 1;
+ }
+ }
+ return 0;
+}
+
+// 传入实际的 index
+int check_valid_formatter(TableInfo *table, int x, int y) {
+ // 合法的公示应该以 = 开头,并且只包含 + - 和
+ char *data = malloc(sizeof(char) * MAX_DATA_LENGTH);
+ strcpy(data, table->data[y][x]);
+ if (data[0] != '=') {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ int length = strlen(data);
+ char *tmp_data = malloc(sizeof(char) * MAX_DATA_LENGTH);
+ for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) {
+ if (data[i] == ' ')
+ continue;
+ // 获取 =,-,+,\n 之间的字符串
+ int j = i;
+ while (j < length && data[j] != '=' && data[j] != '-' &&
+ data[j] != '+' && data[j] != '\n') {
+ tmp_data[j - i] = data[j];
+ j++;
+ }
+ tmp_data[j - i] = '\0';
+ // 判断是否是合法的 index
+ if (tmp_data[0] >= 'A' && tmp_data[0] <= 'Z') {
+ if (!check_index_valid(table, tmp_data))
+ return 0;
+ } else {
+ for (int k = 0; k < j - i; k++) {
+ if (tmp_data[k] < '0' || tmp_data[k] > '9') {
+ return 0;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return 1;
+}
+
+// 获取是行还是列
+int get_index_type(int index) { return index >> 7; }
+
+// 获取具体的值
+int get_index_value(int index) { return index & 0b01111111; }
+
+// 进入选择模式,选择某行或某列
+int start_select_index(int entry) {
+ message = "Select a row or column";
+ current_x = 0;
+ current_y = 1;
+ select_mode = 1;
+ select_entry = entry;
+}
+
+// 退出选择模式
+void end_select_index(TableInfo *table) {
+ // 一个 8 位数字
+ // 最高位: 0 代表行 1 代表列
+ // 低 7 位: 代表行号或列号对应字符的 ASCII 码
+ int select_value = 0;
+ if (current_x == 0) {
+ // x = 0 表示选择行
+ select_value = 0b00000000 | current_y;
+ } else {
+ // x > 0 表示选择列
+ select_value = 0b10000000 | (current_x + 'A' - 1);
+ }
+ int type = get_index_type(select_value);
+ int value = get_index_value(select_value);
+
+ int ascii_sort = 0;
+ // 0 代表不区分大小写,1 代表区分大小写
+ int case_sensitive = 0;
+
+ // 判断是否和数字操作有关
+ if (select_entry == 2 || select_entry == 3 || select_entry == 4 ||
+ select_entry == 5 || select_entry == 6) {
+ int valid = is_index_all_number(table, type, value);
+ if (!valid) {
+ if (select_entry == 6) {
+ ascii_sort = 1;
+ message =
+ "This row or column is not all number, use ASCII to "
+ "sort!\n Do you want to use Case Sensitive? ([Y]/n): ";
+ // 等待完善:选择大小写敏感
+ // char tmp;
+ // input_mode = 1;
+ // scanf("%c", &tmp);
+ // input_mode = 0;
+ // if (tmp == 'n' || tmp == 'N') {
+ // case_sensitive = 0;
+ // } else {
+ // case_sensitive = 1;
+ // }
+ } else {
+ message = "This row or column is not all number!";
+ return;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ if (select_entry == 2) {
+ // sum
+ int sum = 0;
+ if (type == 0) {
+ // 行
+ value = value - 1;
+ for (int i = 0; i < table->current_width; i++) {
+ if (strlen(table->data[value][i]) > 0) {
+ sum += atoi(table->data[value][i]);
+ }
+ }
+ } else {
+ // 列
+ value = value - 'A';
+ for (int i = 0; i < table->current_height; i++) {
+ if (strlen(table->data[i][value]) > 0) {
+ sum += atoi(table->data[i][value]);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ char *tmp_message = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * MAX_MESSAGE_LENGTH);
+ sprintf(tmp_message, "Sum: %d", sum);
+ message = tmp_message;
+ } else if (select_entry == 3) {
+ // average
+ int sum = 0;
+ int count = 0;
+ if (type == 0) {
+ // 行
+ value = value - 1;
+ for (int i = 0; i < table->current_width; i++) {
+ if (strlen(table->data[value][i]) > 0) {
+ sum += atoi(table->data[value][i]);
+ count++;
+ }
+ }
+ } else {
+ // 列
+ value = value - 'A';
+ for (int i = 0; i < table->current_height; i++) {
+ if (strlen(table->data[i][value]) > 0) {
+ sum += atoi(table->data[i][value]);
+ count++;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ char *tmp_message = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * MAX_MESSAGE_LENGTH);
+ sprintf(tmp_message, "Average: %f", (double)sum / count);
+ message = tmp_message;
+ } else if (select_entry == 4) {
+ // max
+ int max_ = -0x7fffffff;
+ if (type == 0) {
+ // 行
+ value = value - 1;
+ for (int i = 0; i < table->current_width; i++) {
+ if (strlen(table->data[value][i]) > 0) {
+ max_ = atoi(table->data[value][i]) > max_
+ ? atoi(table->data[value][i])
+ : max_;
+ }
+ }
+ } else {
+ // 列
+ value = value - 'A';
+ for (int i = 0; i < table->current_height; i++) {
+ if (strlen(table->data[i][value]) > 0) {
+ max_ = atoi(table->data[i][value]) > max_
+ ? atoi(table->data[i][value])
+ : max_;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ char *tmp_message = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * MAX_MESSAGE_LENGTH);
+ sprintf(tmp_message, "Max: %d", max_);
+ message = tmp_message;
+ } else if (select_entry == 5) {
+ // min
+ int min_ = 0x7fffffff;
+ if (type == 0) {
+ // 行
+ value = value - 1;
+ for (int i = 0; i < table->current_width; i++) {
+ if (strlen(table->data[value][i]) > 0) {
+ min_ = atoi(table->data[value][i]) < min_
+ ? atoi(table->data[value][i])
+ : min_;
+ }
+ }
+ } else {
+ // 列
+ value = value - 'A';
+ for (int i = 0; i < table->current_height; i++) {
+ if (strlen(table->data[i][value]) > 0) {
+ min_ = atoi(table->data[i][value]) < min_
+ ? atoi(table->data[i][value])
+ : min_;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ char *tmp_message = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * MAX_MESSAGE_LENGTH);
+ sprintf(tmp_message, "Min: %d", min_);
+ message = tmp_message;
+ } else if (select_entry == 6) {
+ // sort
+ if (type == 0) {
+ // 行
+ value = value - 1;
+ for (int i = 0; i < table->current_width; i++) {
+ for (int j = i + 1; j < table->current_width; j++) {
+ if (!ascii_sort) {
+ if (atoi(table->data[value][i]) >
+ atoi(table->data[value][j])) {
+ changeTwoColumn(table, i, j);
+ }
+ message = "Sorted by number!";
+ } else {
+ if (str_cmp(table->data[value][i],
+ table->data[value][j],
+ case_sensitive) > 0) {
+ changeTwoColumn(table, i, j);
+ }
+ message = "Sorted by ASCII!";
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ } else {
+ // 列
+ value = value - 'A';
+ for (int i = 0; i < table->current_height; i++) {
+ for (int j = i + 1; j < table->current_height; j++) {
+ if (!ascii_sort) {
+ if (atoi(table->data[i][value]) >
+ atoi(table->data[j][value])) {
+ changeTwoRow(table, i, j);
+ }
+ message = "Sorted by number!";
+ } else {
+ if (str_cmp(table->data[i][value],
+ table->data[j][value],
+ case_sensitive) > 0) {
+ changeTwoRow(table, i, j);
+ }
+ message = "Sorted by ASCII!";
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ } else {
+ // 选择行或列
+ if (type == 0) {
+ // 行
+ value = value - 1;
+ char *tmp_message =
+ (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * MAX_MESSAGE_LENGTH);
+ sprintf(tmp_message, "Selected row: %d", value + 1);
+ message = tmp_message;
+ } else {
+ // 列
+ value = value - 'A';
+ char *tmp_message =
+ (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * MAX_MESSAGE_LENGTH);
+ sprintf(tmp_message, "Selected column: %c", value + 'A');
+ message = tmp_message;
+ }
+ }
+
+ // char *tmp_message = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * MAX_MESSAGE_LENGTH);
+ // sprintf(tmp_message, "Selected: %d,%c", get_index_type(select_value),
+ // get_index_value(select_value));
+ // message = tmp_message;
+
+ select_mode = 0;
+ current_y = -1;
+ current_x = select_entry;
+}
+
+// 将 int 转换为字符串
+char *int_to_string(int num) {
+ char *str = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * 100);
+ sprintf(str, "%d", num);
+ return str;
+}
+
+// 初始化表格
+void init_table(int width, int height, int column_width, TableInfo *table) {
+ table->current_width = width;
+ table->current_height = height;
+ for (int i = 0; i < width; i++) {
+ table->column_width[i] = column_width;
+ }
+ for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) {
+ for (int j = 0; j < width; j++) {
+ table->data[i][j][0] = '\0';
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// 计算公式
+int cal_formula(TableInfo *table, int x, int y) {
+ char *data = malloc(sizeof(char) * MAX_DATA_LENGTH);
+ strcpy(data, table->data[y][x]);
+ int length = strlen(data);
+ char *tmp_data = malloc(sizeof(char) * MAX_DATA_LENGTH);
+ int result = 0;
+ for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) {
+ if (data[i] == ' ')
+ continue;
+ // 标注 -
+ int minus = 0;
+ // 获取 =,-,+,\n 之间的字符串
+ int j = i;
+ while (j < length && data[j] != '=' && data[j] != '-' &&
+ data[j] != '+' && data[j] != '\n') {
+ tmp_data[j - i] = data[j];
+ j++;
+ }
+ tmp_data[j - i] = '\0';
+ // 判断是否是 -
+ if (data[i - 1] == '-') {
+ minus = 1;
+ }
+ // 判断是否是合法的 index
+ if (tmp_data[0] >= 'A' && tmp_data[0] <= 'Z') {
+ if (!check_index_valid(table, tmp_data))
+ return -1;
+ // 0 表示 列,剩下的是行
+ int col = tmp_data[0] - 'A';
+ int row = 0;
+ for (int k = 1; k < strlen(tmp_data); k++) {
+ row = row * 10 + tmp_data[k] - '0';
+ }
+ // 判断 table->data[row - 1][col] 是否是数字
+ if (strlen(table->data[row - 1][col]) == 0) {
+ return -1;
+ }
+ if (!is_string_all_number(table->data[row - 1][col])) {
+ return -1;
+ }
+ if (minus) {
+ result -= atoi(table->data[row - 1][col]);
+ } else {
+ result += atoi(table->data[row - 1][col]);
+ }
+ } else {
+ for (int k = 0; k < j - i; k++) {
+ if (tmp_data[k] < '0' || tmp_data[k] > '9') {
+ return -1;
+ }
+ }
+ if (minus) {
+ result -= atoi(tmp_data);
+ } else {
+ result += atoi(tmp_data);
+ }
+ }
+ i += j - i;
+ }
+ return result;
+}
+
+// 输出表格
+void printTable(TableInfo *table) {
+ system("cls");
+ printf("Table v0.2 by Luthics\n");
+ int max_l = int_length(table->current_height) + 1;
+ // render table
+ for (int i = -1; i < table->current_height; i++) {
+ for (int j = -1; j < table->current_width; j++) {
+ printf("+");
+ if (j == -1) {
+ for (int k = 0; k < max_l; k++) {
+ printf("-");
+ }
+ continue;
+ }
+ for (int k = 0; k < table->column_width[j]; k++) {
+ printf("-");
+ }
+ }
+ printf("+\n");
+ if (i == -1) {
+ // 输出 A-Z 的列名
+ for (int j = -1; j < table->current_width; j++) {
+ if (j == -1) {
+ printf("|");
+ for (int k = 0; k < max_l; k++) {
+ printf(" ");
+ }
+ continue;
+ }
+ printf("|");
+ for (int k = 0; k < table->column_width[j] - 1; k++) {
+ printf(" ");
+ }
+ if (select_mode) {
+ if (current_x - 1 == j && current_y == 0) {
+ // RED
+ printf("\033[31m");
+ // BOLD
+ printf("\033[1m");
+ }
+ }
+ printf("%c", 'A' + j);
+ if (select_mode) {
+ if (current_x - 1 == j && current_y == 0) {
+ // RESET
+ printf("\033[0m");
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ printf("|\n");
+ continue;
+ }
+ for (int j = -1; j < table->current_width; j++) {
+ if (j == -1) {
+ printf("|");
+ int data_length = int_length(i + 1);
+ for (int k = 0; k < max_l - data_length; k++) {
+ printf(" ");
+ }
+ if (select_mode) {
+ if (current_x == 0 && current_y == i + 1) {
+ // RED
+ printf("\033[31m");
+ // BOLD
+ printf("\033[1m");
+ }
+ }
+ printf("%d", i + 1);
+ if (select_mode) {
+ if (current_x == 0 && current_y == i + 1) {
+ // RESET
+ printf("\033[0m");
+ }
+ }
+ continue;
+ }
+ printf("|");
+ int data_length =
+ table->data[i][j] == NULL ? 0 : strlen(table->data[i][j]);
+
+ if (data_length == 0) {
+ if (i == current_y && j == current_x && !select_mode) {
+ printf("_");
+ } else {
+ printf(" ");
+ }
+ for (int k = 0; k < table->column_width[j] - 1; k++) {
+ printf(" ");
+ }
+ } else {
+ int formatter = 0;
+ if (table->data[i][j][0] == '=') {
+ formatter = 1;
+ }
+ int add_ = 0;
+ if (select_mode) {
+ if (current_x == j + 1 || current_y == i + 1) {
+ // RED
+ printf("\033[31m");
+ // BOLD
+ printf("\033[1m");
+ }
+ } else if (i == current_y && j == current_x) {
+ // RED
+ printf("\033[31m");
+ // BOLD
+ printf("\033[1m");
+ } else if (formatter) {
+ // BLUE
+ printf("\033[34m");
+ // BOLD
+ printf("\033[1m");
+ }
+ int formatter_success = 0;
+ if (formatter && !select_mode &&
+ !(i == current_y && j == current_x)) {
+ // todo 先计算后渲染,修复列宽不合适的bug
+ int data = cal_formula(table, j, i);
+ if (data == -1) {
+ formatter_success = 0;
+ } else {
+ char *tmp_data =
+ (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * MAX_DATA_LENGTH);
+ sprintf(tmp_data, "%d", data);
+ data_length = strlen(tmp_data);
+ printf("%s", tmp_data);
+ table->column_width[j] =
+ max(table->column_width[j], strlen(tmp_data));
+ formatter_success = 1;
+ }
+ }
+ if (!formatter_success) {
+ for (int k = 0; k < data_length; k++) {
+ printf("%c", table->data[i][j][k]);
+ }
+ }
+ if (select_mode) {
+ if (current_x == j + 1 || current_y == i + 1) {
+ // RESET
+ printf("\033[0m");
+ }
+ } else if (i == current_y && j == current_x) {
+ // RESET
+ printf("\033[0m");
+ // 如果还有空间,就补上下划线
+ if (table->column_width[j] - data_length > 0) {
+ printf("_");
+ add_ = 1;
+ }
+ } else if (formatter) {
+ // Reset
+ printf("\033[0m");
+ }
+ if (formatter) {
+ // 补上空格
+ for (int k = 0; k < table->column_width[j] - data_length;
+ k++) {
+ printf(" ");
+ }
+ } else {
+ for (int k = 0;
+ k < table->column_width[j] - data_length - add_; k++) {
+ printf(" ");
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ printf("|\n");
+ }
+ for (int j = -1; j < table->current_width; j++) {
+ if (j == -1) {
+ printf("+");
+ for (int k = 0; k < max_l; k++) {
+ printf("-");
+ }
+ continue;
+ }
+ printf("+");
+ for (int k = 0; k < table->column_width[j]; k++) {
+ printf("-");
+ }
+ }
+ printf("+\n");
+
+ // render functions
+ for (int i = 0; i < FUNCTION_NUM; i++) {
+ if (current_y == -1 && i == current_x) {
+ // RED
+ printf("\033[31m");
+ // BOLD
+ printf("\033[1m");
+ }
+ printf("%s", functions[i]);
+ if (current_y == -1 && i == current_x) {
+ // RESET
+ printf("\033[0m");
+ }
+ if (i != FUNCTION_NUM - 1) {
+ printf(" ");
+ }
+ }
+ printf("\n");
+ printf("%s\n", message);
+}
+
+// 判断数据文件是否存在
+int is_data_file_exist() {
+ FILE *fp = fopen("table.dat", "r");
+ if (fp == NULL) {
+ return 0;
+ } else {
+ fclose(fp);
+ return 1;
+ }
+}
+
+// 从文件中读取表格信息
+TableInfo load_table_from_file(char *filename) {
+ TableInfo table;
+ FILE *fp = fopen(filename, "r");
+ fread(&table, sizeof(TableInfo), 1, fp);
+ fclose(fp);
+ return table;
+}
+
+// 将表格信息写入文件
+int save_table_to_file(char *filename, TableInfo table) {
+ FILE *fp = fopen(filename, "w");
+ fwrite(&table, sizeof(TableInfo), 1, fp);
+ fclose(fp);
+ return 0;
+}
+
+// 设置单元格的值
+void setCell(TableInfo *table, int row, int column, char *data) {
+ if (row >= table->current_height || column >= table->current_width ||
+ row < 0 || column < 0) {
+ return;
+ }
+ strcpy(table->data[row][column], data);
+ if (strlen(data) > table->column_width[column]) {
+ table->column_width[column] = strlen(data);
+ }
+}
+
+// 获取单元格的值
+int get_max_width_in_a_column(TableInfo *table, int column) {
+ int max_width = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < table->current_height; i++) {
+ int data_length =
+ table->data[i][column] == NULL ? 0 : strlen(table->data[i][column]);
+ if (data_length > max_width) {
+ max_width = data_length;
+ }
+ }
+ return max(max_width, table->column_width[column]);
+}
+
+// 向单元格中添加字符
+void add_char_to_cell(TableInfo *table, int row, int column, char c) {
+ if (row >= table->current_height || column >= table->current_width ||
+ row < 0 || column < 0) {
+ return;
+ }
+ int data_length = strlen(table->data[row][column]);
+ if (data_length < MAX_DATA_LENGTH - 1) {
+ table->data[row][column][data_length] = c;
+ table->data[row][column][data_length + 1] = '\0';
+ table->column_width[column] = get_max_width_in_a_column(table, column);
+ }
+}
+
+// 从单元格中删除字符
+void del_char_from_cell(TableInfo *table, int row, int column) {
+ if (row >= table->current_height || column >= table->current_width ||
+ row < 0 || column < 0) {
+ return;
+ }
+ int data_length = strlen(table->data[row][column]);
+ if (data_length > 0) {
+ table->data[row][column][data_length - 1] = '\0';
+ table->column_width[column] = get_max_width_in_a_column(table, column);
+ }
+}
+
+// 返回 1 代表响应成功
+// 返回 0 代表响应失败
+int handleKeyPress(int key, TableInfo *table) {
+ int status = 0;
+ if (key == 224) { // 特殊键
+ key = getch(); // 获取特殊键码
+ if (key == KEY_LEFT_ARROW) {
+ if (select_mode) {
+ // 选择模式,0,0是左上角,0,1 0,2 0,3 代表每行行号 1,0 2,0 3,0
+ // 代表每列列号
+ if (current_y == 0) {
+ if (current_x > 1)
+ current_x--;
+ else
+ current_x = table->current_width;
+ }
+ if (current_x == 0) {
+ current_y = 0;
+ current_x = table->current_width;
+ }
+ status = 1;
+ } else {
+ if (current_x > 0) {
+ current_x--;
+ } else if (current_x == 0) {
+ if (current_y == -1) {
+ current_x = FUNCTION_NUM - 1;
+ } else {
+ current_x = table->current_width - 1;
+ }
+ }
+ status = 1;
+ }
+ }
+ if (key == KEY_RIGHT_ARROW) {
+ if (select_mode) {
+ if (current_y == 0) {
+ if (current_x < table->current_width)
+ current_x++;
+ else
+ current_x = 1;
+ }
+ if (current_x == 0) {
+ current_y = 0;
+ current_x = 1;
+ }
+ status = 1;
+ } else {
+ if (current_y == -1) {
+ current_x = (current_x + 1) % FUNCTION_NUM;
+ } else {
+ current_x = (current_x + 1) % table->current_width;
+ }
+ status = 1;
+ }
+ }
+ if (key == KEY_UP_ARROW) {
+ if (select_mode) {
+ if (current_x == 0) {
+ if (current_y > 1)
+ current_y--;
+ else
+ current_y = table->current_height;
+ }
+ if (current_y == 0) {
+ current_x = 0;
+ current_y = table->current_height;
+ }
+ status = 1;
+ } else {
+ if (current_y > 0) {
+ current_y--;
+ } else if (current_y == 0) {
+ current_y = -1;
+ current_x = min(FUNCTION_NUM - 1, current_x);
+ } else if (current_y == -1) {
+ current_y = table->current_height - 1;
+ current_x = min(table->current_width - 1, current_x);
+ }
+ status = 1;
+ }
+ }
+ if (key == KEY_DOWN_ARROW) {
+ if (select_mode) {
+ if (current_x == 0) {
+ if (current_y < table->current_height)
+ current_y++;
+ else
+ current_y = 1;
+ }
+ if (current_y == 0) {
+ current_x = 0;
+ current_y = 1;
+ }
+ status = 1;
+ } else {
+ if (current_y < table->current_height - 1 && current_y >= 0) {
+ current_y++;
+ } else if (current_y == table->current_height - 1) {
+ // TO FUNCTIONS AREA
+ current_y = -1;
+ current_x = min(FUNCTION_NUM - 1, current_x);
+ } else if (current_y == -1) {
+ current_y = 0;
+ current_x = min(table->current_width - 1, current_x);
+ }
+ status = 1;
+ }
+ }
+ } else {
+ // ctrl + c
+ if (key == 3) {
+ alive = 0;
+ message = "Bye!";
+ status = 1;
+ }
+ // ctrl + s
+ if (key == 19) {
+ save_table_to_file("table.dat", *table);
+ message = "Saved!";
+ status = 1;
+ }
+ if (select_mode) {
+ // ENTER
+ if (key == KEY_ENTER) {
+ end_select_index(table);
+ status = 1;
+ }
+ // ESC
+ if (key == KEY_ESC) {
+ select_mode = 0;
+ current_y = -1;
+ current_x = select_entry;
+ message = "Canceled!";
+ status = 1;
+ }
+ } else {
+ // 判断 key 是可打印字符
+ if (key >= 32 && key <= 126) {
+ add_char_to_cell(table, current_y, current_x, key);
+ status = 1;
+ }
+ // 退格键
+ if (key == 8) {
+ del_char_from_cell(table, current_y, current_x);
+ status = 1;
+ }
+ // ENTER
+ if (key == KEY_ENTER) {
+ if (current_y == -1) {
+ if (current_x == 0) {
+ save_table_to_file("table.dat", *table);
+ message = "Saved!";
+ }
+ if (current_x == 1) {
+ *table = load_table_from_file("table.dat");
+ message = "Loaded!";
+ }
+ if (current_x == 2) {
+ start_select_index(2);
+ }
+ if (current_x == 3) {
+ start_select_index(3);
+ }
+ if (current_x == 4) {
+ start_select_index(4);
+ }
+ if (current_x == 5) {
+ start_select_index(5);
+ }
+ if (current_x == 6) {
+ start_select_index(6);
+ }
+ if (current_x == 7) {
+ alive = 0;
+ message = "Bye!";
+ }
+ } else {
+ // 如果以 = 开头
+ if (table->data[current_y][current_x][0] == '=') {
+ if (!check_valid_formatter(table, current_x,
+ current_y)) {
+ message = "Not a valid formatter!";
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ int debug = 0;
+ if (debug) {
+ char *tmp_message = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * MAX_MESSAGE_LENGTH);
+ sprintf(tmp_message, "x: %d, y: %d", current_x, current_y);
+ message = tmp_message;
+ }
+ return status;
+}
+
+int main() {
+ TableInfo table;
+ int load_from_file = 0;
+
+ // 先判断是否有数据文件
+ if (is_data_file_exist()) {
+ char tmp;
+ // 询问是否从文件中读取
+ printf("Load from file? ([Y]/n): ");
+ scanf("%c", &tmp);
+ if (tmp == 'n' || tmp == 'N') {
+ load_from_file = 0;
+ } else {
+ load_from_file = 1;
+ }
+ }
+ if (load_from_file) {
+ table = load_table_from_file("table.dat");
+ } else {
+ // 创建新表格
+ printf("Let's create a table!\n");
+ int width = 0, height = 0;
+ int column_width = 0;
+ while (width <= 0 || width > MAX_COLUMN) {
+ printf("Input width (1-%d): ", MAX_COLUMN);
+ scanf("%d", &width);
+ }
+ while (height <= 0 || height > MAX_ROW) {
+ printf("Input height (1-%d): ", MAX_ROW);
+ scanf("%d", &height);
+ }
+ while (column_width <= 0 || column_width > MAX_COLUMN_WIDTH) {
+ printf("Input column width (1-%d): ", MAX_COLUMN_WIDTH);
+ scanf("%d", &column_width);
+ }
+
+ init_table(width, height, column_width, &table);
+ }
+ // 把第一行第一列的单元格设置为 Hello
+ setCell(&table, 0, 0, "Hello");
+
+ // 主循环
+ while (alive) {
+ printTable(&table);
+ // drawGUI(currentSelection);
+
+ int keyPressed = getch(); // 获取键盘输入
+ handleKeyPress(keyPressed, &table);
+
+ // tick = (tick + 1) % MAX_TICK;
+ }
+
+ // 询问是否保存
+ int save_to_file = 0;
+ char tmp;
+ printf("Save to file? ([Y]/n): ");
+ scanf("%c", &tmp);
+ if (tmp == 'n' || tmp == 'N') {
+ save_to_file = 0;
+ } else {
+ save_to_file = 1;
+ }
+ if (save_to_file) {
+ save_table_to_file("table.dat", table);
+ }
+ return 0;
+}
+设在初始状态下在国际象棋的棋盘上没有任何棋子(这里的棋子指皇后棋子)。然后顺序在第1行,第2行……第8行上布放棋子。在每一行中共有8个可选择的位置,但在任一时刻棋盘的合法布局都必须满足3个限制条件
编写求解并输出此问题的一个合法布局的程序。
+在第i行布放棋子时,从第1列到第8列逐列考察。当在第i行第j列布放棋子时,需要考察布放棋子后在行方向、列方向、正斜线和反斜线方向上的布局状态是否合法,若该棋子布放合法,再递归求解在第i+1行布放棋子;若该棋子布放不合法,移去这个棋子,恢复布放该棋子前的状态,然后再试探在第i行第j+1列布放棋子。
使用回溯法,从第一行开始,每一行都有 n 个选择,如果选择合法,就继续下一行,否则就回溯到上一行,重新选择。
参考 洛谷 P1219 实现的 n 皇后问题
#include <stdio.h>
+#include <stdlib.h>
+
+// 每行每列每个对角线是否被占用
+int ans, a[10005];
+int n;
+int cx[100], zx[100], col[100];
+
+void pt() {
+ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
+ for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
+ if (a[i] == j) {
+ printf("Q");
+ } else {
+ printf(".");
+ }
+ }
+ printf("\n");
+ }
+ printf("\n");
+ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
+ printf("%d ", a[i]);
+ }
+ printf("\n");
+}
+
+// 回溯法
+void dfs(int x) {
+ if (x > n) {
+ ans++;
+ if (ans <= 3) {
+ pt();
+ // for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
+ // printf("%d ", a[i]);
+ // }
+ // printf("\n");
+ }
+ return;
+ }
+ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
+ int l = x + i, r = x - i + 15;
+ // 如果这一列、这一正对角线、这一反对角线都没有被占用
+ if (cx[r] == 0 && zx[l] == 0 && col[i] == 0) {
+ a[x] = i;
+ cx[r] = 1;
+ zx[l] = 1;
+ col[i] = 1;
+ dfs(x + 1);
+ cx[r] = 0;
+ zx[l] = 0;
+ col[i] = 0;
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+int main() {
+ scanf("%d", &n);
+ dfs(1);
+ printf("%d", ans);
+ return 0;
+}
+
+// Ref: P1219 [USACO1.5] 八皇后 Checker Challenge
+// https://www.luogu.com.cn/record/40132197
+8
+仅输出前三个解
+Q.......
+....Q...
+.......Q
+.....Q..
+..Q.....
+......Q.
+.Q......
+...Q....
+
+1 5 8 6 3 7 2 4
+Q.......
+.....Q..
+.......Q
+..Q.....
+......Q.
+...Q....
+.Q......
+....Q...
+
+1 6 8 3 7 4 2 5
+Q.......
+......Q.
+...Q....
+.....Q..
+.......Q
+.Q......
+....Q...
+..Q.....
+
+1 7 4 6 8 2 5 3
+92
+12
+仅输出前三个解
+Q...........
+..Q.........
+....Q.......
+.......Q....
+.........Q..
+...........Q
+.....Q......
+..........Q.
+.Q..........
+......Q.....
+........Q...
+...Q........
+
+1 3 5 8 10 12 6 11 2 7 9 4
+Q...........
+..Q.........
+....Q.......
+.........Q..
+.......Q....
+..........Q.
+.Q..........
+...........Q
+.....Q......
+........Q...
+......Q.....
+...Q........
+
+1 3 5 10 8 11 2 12 6 9 7 4
+Q...........
+..Q.........
+....Q.......
+.........Q..
+.......Q....
+..........Q.
+.Q..........
+...........Q
+......Q.....
+........Q...
+...Q........
+.....Q......
+
+1 3 5 10 8 11 2 12 7 9 4 6
+14200
+设编号为1,2,…,n(n>0)个人按顺时针方向围坐一圈,每人持有一个正整数密码。开始时任意给出一个报数上限m,从第一个人开始顺时针方向自1起顺序报数,报到m时停止报数,报m的人出列,将他的密码作为新的m值,从他在顺时针方向上的下一个人起重新自1报数;如此下去直到所有人全部出列为止。
设计一个程序模拟此过程,给出出列人的编号序列。
+可考虑不带头结点的单链表结构。
+N=7,七个人的密码依次为3,1,7,2,4,8,4.
+初始报数上限值m=20。
使用循环链表,每次报数到 m 时,就删除这个节点,然后从下一个节点开始重新报数,直到报到这个节点对应的数字,再次循环。
+#include <stdio.h>
+#include <stdlib.h>
+
+int rs[105]; // 每个人的状态
+int n; // 人数
+
+int xcz; // 剩余人数
+int m[105], m0; // 间隔
+
+int zj(int a) {
+ // 寻找下一个活着的人
+ a++;
+ if (a > n)
+ a -= n;
+ while (rs[a] == 0 && xcz > 0) {
+ a++;
+ if (a > n)
+ a -= n;
+ }
+ return a;
+}
+
+int main() {
+ freopen("data.in", "r", stdin);
+ scanf("%d%d", &n, &m0);
+ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
+ scanf("%d", &m[i]);
+ xcz = n;
+ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
+ // 把每个人设置为活着
+ rs[i] = 1;
+ while (m0 > n) {
+ m0 -= n;
+ }
+ for (int i = m0; xcz > 0;) {
+ if (rs[i] == 1) {
+ rs[i] = 0;
+ xcz--;
+ printf("%d ", i);
+ }
+ int ls = m[i];
+ // printf("ls=%d\n", ls);
+ while (ls--)
+ i = zj(i);
+ }
+ return 0;
+}
+
+// Ref: P1996 约瑟夫问题
+// 已修改为实验版本
+7 20
+3 1 7 2 4 8 4
+6 1 4 7 2 3 5
+大学的每个专业都要制定教学计划。假设任何专业都有固定的学习年 +限,每学年含两学期,每学期的时间长度和学分上限值均相等。每个专业 +开设的课程都是固定的,而且课程在开设时间的安排必须满足先修关系。 +每门课程有哪些先修课程是确定的,可以有任意多门,也可以没有。每门 +课恰好占一个学期。试在这样的前提下设计一个教学计划编制程序。
+可设学期总数不超过12,课程总数小于100。如果输入的先修课程号不在该专业开设的课程序列中,则作为错误处理。
+使用拓扑排序,先将课程按照先修课程的数量进行排序,先修课程数量越多的课程越靠前,然后从前往后,如果学期学习数量小于平均值,则将前面的课程往后移动。
+#include <bits/stdc++.h>
+
+using namespace std;
+
+int se; // 学期总数
+int sx; // 学分上限
+int cl; // 课程数量
+int ren[12], fe[12], re[12][105];
+
+struct Class {
+ string id; // 课程编号
+ int sx; // 学分
+ int xq;
+ int sel; // 是否已经选择
+ int pren, nexn; // 先修课程数量
+ int ppren; // use for topo
+ string pre[105]; // 先修课程
+ string next[105]; // 后续课程
+} ss[105];
+
+// 输出具体的课程安排
+void pt(int detail = 0) {
+ // print
+ for (int i = 0; i < cl; i++) {
+ cout << ss[i].id << " " << ss[i].sx << " " << ss[i].pren << " "
+ << ss[i].nexn << endl;
+ if (!detail)
+ continue;
+ if (ss[i].pren > 0) {
+ cout << "pre:" << endl;
+ for (int j = 0; j < ss[i].pren; j++) {
+ cout << ss[i].pre[j] << " ";
+ }
+ cout << endl;
+ }
+ if (ss[i].nexn > 0) {
+ cout << "next:" << endl;
+ for (int j = 0; j < ss[i].nexn; j++) {
+ cout << ss[i].next[j] << " ";
+ }
+ cout << endl;
+ }
+ cout << endl;
+ }
+}
+
+// 寻找 id
+int fd(string id) {
+ for (int i = 0; i < cl; i++) {
+ if (ss[i].id == id) {
+ return i;
+ }
+ }
+ return -1;
+}
+
+// 去除字符串两边空格和换行符
+string ql(string s) {
+ int l = 0, r = s.length() - 1;
+ while (s[l] == ' ' || s[l] == '\n')
+ l++;
+ while (s[r] == ' ' || s[r] == '\n')
+ r--;
+ return s.substr(l, r - l + 1);
+}
+
+// 寻找先修课程的最迟学期
+int xz(int i) {
+ // cout << ss[i].id << " " << ss[i].pren << endl;
+ if (ss[i].pren == 0)
+ return 0;
+ int maxn = 0;
+ for (int j = 0; j < ss[i].pren; j++) {
+ int fid = fd(ss[i].pre[j]);
+ if (ss[fid].xq > maxn) {
+ maxn = ss[fid].xq;
+ }
+ }
+ return maxn + 1;
+}
+
+// 寻找后修课程的最早学期
+int xz2(int i) {
+ if (ss[i].nexn == 0)
+ return se;
+ int minn = se;
+ for (int j = 0; j < ss[i].nexn; j++) {
+ int fid = fd(ss[i].next[j]);
+ if (ss[fid].xq < minn) {
+ minn = ss[fid].xq;
+ }
+ }
+ return minn;
+}
+// 拓扑排序,将排好序的id 放入sorted
+void topo() {
+ int sorted[105] = {0};
+ int cnt = 0;
+ queue<Class *> q;
+ for (int i = 0; i < cl; i++) {
+ if (ss[i].ppren == 0) {
+ q.push(&ss[i]);
+ }
+ }
+ while (!q.empty()) {
+ Class *tmp = q.front();
+ sorted[cnt] = fd(tmp->id);
+ q.pop();
+ cnt++;
+ for (int i = 0; i < tmp->nexn; i++) {
+ ss[fd(tmp->next[i])].ppren--;
+ if (ss[fd(tmp->next[i])].ppren == 0) {
+ q.push(&ss[fd(tmp->next[i])]);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ if (cnt != cl) {
+ cout << "error" << endl;
+ exit(0);
+ }
+ Class newss[105];
+ // 将 ss 顺序改为 sorted 顺序
+ for (int i = 0; i < cl; i++) {
+ newss[i] = ss[sorted[i]];
+ }
+ for (int i = 0; i < cl; i++) {
+ ss[i] = newss[i];
+ }
+}
+
+void avgf() {
+ // 计算平均每学期学习数量
+ int avg = cl / se;
+ // cout << avg << endl;
+ // 按从后向前,如果学期学习数量小于平均值,则将前面的课程往后移动
+ for (int i = se - 1; i >= 1; i--) {
+ if (ren[i] < avg) {
+ for (int j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
+ // cout << j << " " << ren[j] << endl;
+ if (ren[j] <= 0)
+ continue;
+ int flag = 0;
+ for (int ii = 0; ii < ren[j] && ren[i] < avg; ii++) {
+ int c = re[j][ii];
+ // cout << " " << ss[c].id << " " << xz2(2)<< endl;
+ // cout << c << endl;
+ if (xz2(c) > i) {
+ // 把 c 课程放到 i 学期
+ re[i][ren[i]++] = c;
+ ss[c].xq = i;
+ // 把 c 课程从 j 学期删除
+ for (int jj = ii; jj < ren[j] - 1; jj++) {
+ re[j][jj] = re[j][jj + 1];
+ }
+ ren[j]--;
+ flag = 1;
+ }
+ // 如果 i 学期中的课程数量大于平均值,则跳出循环
+ if (ren[i] >= avg) {
+ break;
+ }
+ if (flag == 1) {
+ ii = -1;
+ flag = 0;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// 输出最终结果
+void pte() {
+ for (int i = 0; i < se; i++) {
+ if (ren[i] == 0)
+ continue;
+ cout << "学期 " << i + 1 << " 学分 " << fe[i] << " 课程数 " << ren[i]
+ << " 课程:";
+ for (int j = 0; j < ren[i]; j++) {
+ cout << ss[re[i][j]].id << " ";
+ }
+ cout << endl;
+ }
+}
+
+int main() {
+ freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
+ cin >> se >> sx;
+ if (se <= 0 || sx <= 0 || se > 6 || sx > 10) {
+ cout << "error" << endl;
+ exit(0);
+ }
+ cin >> cl;
+ if (cl <= 0 || cl > 12) {
+ cout << "error" << endl;
+ exit(0);
+ }
+ for (int i = 0; i < cl; i++) {
+ cin >> ss[i].id;
+ ss[i].id = ql(ss[i].id);
+ }
+ for (int i = 0; i < cl; i++) {
+ // 学分和前置课程
+ cin >> ss[i].sx >> ss[i].pren;
+ ss[i].ppren = ss[i].pren;
+ for (int j = 0; j < ss[i].pren; j++) {
+ string tmp;
+ cin >> tmp;
+ tmp = ql(tmp);
+ if (tmp.size() == 0)
+ continue;
+ int fid = fd(tmp);
+ if (fid == -1) {
+ cout << "error" << endl;
+ exit(0);
+ }
+ ss[i].pre[j] = ss[fid].id;
+ ss[fid].next[ss[fid].nexn++] = ss[i].id;
+ }
+ }
+ // pt(1);
+ topo();
+ // pt(1);
+ for (int i = 0; i < cl; i++) {
+ ss[i].xq = xz(i);
+ }
+ int ttc = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < se; i++) {
+ for (int j = 0; j < cl; j++) {
+ // 判断是否已选择
+ if (ss[j].sel == 1) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ // 判断是否学分超过上限
+ if (ss[j].sx + fe[i] > sx) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ // 判断是否先修课程已经学习
+ int flag = 0;
+ for (int k = 0; k < ss[j].pren; k++) {
+ int fid = fd(ss[j].pre[k]);
+ if (ss[fid].sel == 0) {
+ flag = 1;
+ break;
+ }
+ }
+ if (flag == 1) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ // 选择该课程
+ ss[j].sel = 1;
+ fe[i] += ss[j].sx;
+ re[i][ren[i]++] = j;
+ ttc++;
+ }
+ }
+ // 判断是否全部选中
+ if (ttc != cl) {
+ cout << "error" << endl;
+ exit(0);
+ }
+ // for (int i = 0; i < cl; i++) {
+ // cout << ss[i].id << " " << ss[i].xq << endl;
+ // }
+ // pte();
+ int kind;
+ cin >> kind;
+ if (kind != 1 && kind != 2) {
+ cout << "error" << endl;
+ exit(0);
+ }
+ // 输入分配方式,1是负担均匀,2是尽早学习
+ if (kind == 1) {
+ avgf();
+ } else if (kind == 2) {
+ // 本来就是今早分配的,无需更改
+ } else {
+ cout << "error" << endl;
+ exit(0);
+ }
+ // 输出最终结果
+ pte();
+ return 0;
+}
+平均负载
+6 10
+12
+C01 C02 C03 C04 C05 C06 C07 C08 C09 C10 C11 C12
+2 0
+3 1 C01
+4 2 C01 C02
+3 1 C01
+2 2 C03 C04
+3 1 C11
+4 2 C03 C05
+4 2 C03 C06
+7 0
+5 1 C09
+2 1 C09
+3 3 C01 C09 C10
+1
+学期 1 学分 9 课程数 2 课程:C01 C09
+学期 2 学分 8 课程数 2 课程:C02 C11
+学期 3 学分 9 课程数 2 课程:C03 C04
+学期 4 学分 8 课程数 2 课程:C05 C10
+学期 5 学分 8 课程数 2 课程:C12 C06
+学期 6 学分 0 课程数 2 课程:C08 C07
+尽早学完
+6 10
+12
+C01 C02 C03 C04 C05 C06 C07 C08 C09 C10 C11 C12
+2 0
+3 1 C01
+4 2 C01 C02
+3 1 C01
+2 2 C03 C04
+3 1 C11
+4 2 C03 C05
+4 2 C03 C06
+7 0
+5 1 C09
+2 1 C09
+3 3 C01 C09 C10
+2
+学期 1 学分 9 课程数 2 课程:C01 C09
+学期 2 学分 8 课程数 3 课程:C02 C04 C11
+学期 3 学分 9 课程数 2 课程:C10 C03
+学期 4 学分 8 课程数 3 课程:C12 C06 C05
+学期 5 学分 8 课程数 2 课程:C08 C07
+分别采用二叉链表和顺序表作存储结构,实现对二叉排序树与平衡二叉树的操作。
+用二叉链表作存储结构实现二叉排序树。
+用顺序表(一维数组)作存储结构----静态链表
+用二叉链表作存储结构实平衡的二叉排序树。
+#include <stdio.h>
+#include <stdlib.h>
+
+typedef struct Tree {
+ int val;
+ struct Tree *l, *r;
+ struct Tree *parent;
+} Tree;
+
+int n;
+int m;
+
+void makeTree(Tree *root, int val) {
+ if (val < root->val) {
+ if (root->l == NULL) {
+ root->l = (Tree *)malloc(sizeof(Tree));
+ root->l->val = val;
+ root->l->l = NULL;
+ root->l->r = NULL;
+ root->l->parent = root;
+ } else {
+ makeTree(root->l, val);
+ }
+ } else {
+ if (root->r == NULL) {
+ root->r = (Tree *)malloc(sizeof(Tree));
+ root->r->val = val;
+ root->r->l = NULL;
+ root->r->r = NULL;
+ root->r->parent = root;
+ } else {
+ makeTree(root->r, val);
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// 中序遍历
+void inOrder(Tree *root) {
+ if (root == NULL)
+ return;
+ inOrder(root->l);
+ printf("%d ", root->val);
+ inOrder(root->r);
+}
+
+// 二叉排序树T查找成功的平均查找长度
+double ASL(Tree *root, int level) {
+ if (root == NULL)
+ return 0;
+ return level + ASL(root->l, level + 1) + ASL(root->r, level + 1);
+}
+
+// 找到二叉树中值为val的节点并删除
+void delNode(Tree *root, int val) {
+ if (root == NULL)
+ return;
+ if (root->val == val) {
+ if (root->l == NULL && root->r == NULL) {
+ if (root->parent->l == root) {
+ root->parent->l = NULL;
+ } else {
+ root->parent->r = NULL;
+ }
+ free(root);
+ } else if (root->l == NULL) {
+ if (root->parent->l == root) {
+ root->parent->l = root->r;
+ } else {
+ root->parent->r = root->r;
+ }
+ free(root);
+ } else if (root->r == NULL) {
+ if (root->parent->l == root) {
+ root->parent->l = root->l;
+ } else {
+ root->parent->r = root->l;
+ }
+ free(root);
+ } else {
+ Tree *p = root->r;
+ while (p->l != NULL) {
+ p = p->l;
+ }
+ root->val = p->val;
+ delNode(p, p->val);
+ }
+ } else if (root->val > val) {
+ delNode(root->l, val);
+ } else {
+ delNode(root->r, val);
+ }
+}
+
+void pt(Tree *root) {
+ printf("inOrder:\n");
+ inOrder(root);
+ printf("\n");
+ printf("ASL: %lf\n", ASL(root, 1) / n);
+ printf("\n");
+}
+
+int main() {
+ freopen("data.in", "r", stdin);
+ scanf("%d", &n);
+ Tree *root = (Tree *)malloc(sizeof(Tree));
+ root->parent = NULL;
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ int val;
+ scanf("%d", &val);
+ if (i == 0) {
+ root->val = val;
+ root->l = NULL;
+ root->r = NULL;
+ } else {
+ makeTree(root, val);
+ }
+ }
+ pt(root);
+
+ scanf("%d", &m);
+ for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
+ int x;
+ scanf("%d", &x);
+ delNode(root, x);
+ pt(root);
+ }
+ return 0;
+}
+10
+2 5 10 8 7 9 4 6 1 3
+3
+2
+5
+9
+inOrder:
+1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
+ASL: 3.500000
+
+inOrder:
+1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
+ASL: 3.100000
+
+inOrder:
+1 3 4 6 7 8 9 10
+ASL: 2.500000
+
+inOrder:
+1 3 4 6 7 8 10
+ASL: 2.000000
+#include <stdio.h>
+#include <stdlib.h>
+
+int n;
+int m;
+// 二叉排序树,根节点为 1,左子树为 2 * i,右子树为 2 * i + 1
+int tree[1000];
+
+void makeTree(int val) {
+ int r = 1;
+ while (1) {
+ if (val < tree[r]) {
+ if (tree[2 * r] == 0) {
+ // printf("r: %d, val: %d\n", 2 * r, val);
+ tree[2 * r] = val;
+ break;
+ } else {
+ r = 2 * r;
+ }
+ } else {
+ if (tree[2 * r + 1] == 0) {
+ // printf("r: %d, val: %d\n", 2 * r + 1, val);
+ tree[2 * r + 1] = val;
+ break;
+ } else {
+ r = 2 * r + 1;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// 中序遍历
+void inOrder(int root) {
+ if (tree[2 * root] != 0)
+ inOrder(2 * root);
+ printf("%d ", tree[root]);
+ if (tree[2 * root + 1] != 0)
+ inOrder(2 * root + 1);
+}
+
+// 二叉排序树T查找成功的平均查找长度
+double ASL(int root, int level) {
+ if (tree[root] == 0)
+ return 0;
+ return level + ASL(2 * root, level + 1) + ASL(2 * root + 1, level + 1);
+}
+
+// 找到二叉树中值为val的节点并删除
+void delNode(int root, int x) {
+ if (tree[root] == 0)
+ return;
+ if (tree[root] == x) {
+ if (tree[2 * root] == 0 && tree[2 * root + 1] == 0) {
+ tree[root] = 0;
+ } else if (tree[2 * root] != 0 && tree[2 * root + 1] == 0) {
+ tree[root] = tree[2 * root];
+ tree[2 * root] = 0;
+ } else if (tree[2 * root] == 0 && tree[2 * root + 1] != 0) {
+ tree[root] = tree[2 * root + 1];
+ tree[2 * root + 1] = 0;
+ } else {
+ int r = 2 * root + 1;
+ while (tree[2 * r] != 0) {
+ r = 2 * r;
+ }
+ tree[root] = tree[r];
+ tree[r] = 0;
+ }
+ } else if (tree[root] > x) {
+ delNode(2 * root, x);
+ } else {
+ delNode(2 * root + 1, x);
+ }
+}
+
+void pt() {
+ printf("inOrder:\n");
+ inOrder(1);
+ printf("\n");
+ printf("ASL: %lf\n", ASL(1, 1) / n);
+ printf("\n");
+}
+
+int main() {
+ freopen("data.in", "r", stdin);
+ scanf("%d", &n);
+ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
+ int val;
+ scanf("%d", &val);
+ if (i == 1) {
+ tree[1] = val;
+ } else {
+ makeTree(val);
+ }
+ }
+ pt();
+
+ scanf("%d", &m);
+ for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
+ int x;
+ scanf("%d", &x);
+ delNode(1, x);
+ pt();
+ }
+ return 0;
+}
+10 +2 5 10 8 7 9 4 6 1 3 +3 +2 +5 +9
+inOrder:
+1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
+ASL: 3.500000
+
+inOrder:
+1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
+ASL: 3.100000
+
+inOrder:
+1 3 4 6 7 8 9 10
+ASL: 2.500000
+
+inOrder:
+1 3 4 6 7 8 10
+ASL: 2.000000
+#include <stdio.h>
+#include <stdlib.h>
+
+typedef struct Tree {
+ int val;
+ struct Tree *l, *r;
+ struct Tree *parent;
+ int height;
+ int balance;
+} Tree;
+
+int n;
+int m;
+
+// 获取节点高度
+int getHeight(Tree *root) {
+ if (root == NULL)
+ return 0;
+ return root->height;
+}
+
+// 更新节点高度和平衡因子
+void updateHeight(Tree *root) {
+ if (root == NULL)
+ return;
+ int l = getHeight(root->l);
+ int r = getHeight(root->r);
+ root->height = (l > r ? l : r) + 1;
+ root->balance = l - r;
+}
+
+// 左旋操作
+Tree *leftRotate(Tree *root) {
+ Tree *newRoot = root->r;
+ root->r = newRoot->l;
+ if (newRoot->l != NULL)
+ newRoot->l->parent = root;
+ newRoot->l = root;
+ newRoot->parent = root->parent;
+ root->parent = newRoot;
+ updateHeight(root);
+ updateHeight(newRoot);
+ return newRoot;
+}
+
+// 右旋操作
+Tree *rightRotate(Tree *root) {
+ Tree *newRoot = root->l;
+ root->l = newRoot->r;
+ if (newRoot->r != NULL)
+ newRoot->r->parent = root;
+ newRoot->r = root;
+ newRoot->parent = root->parent;
+ root->parent = newRoot;
+ updateHeight(root);
+ updateHeight(newRoot);
+ return newRoot;
+}
+
+// 左右旋操作
+Tree *leftRightRotate(Tree *root) {
+ root->l = leftRotate(root->l);
+ return rightRotate(root);
+}
+
+// 右左旋操作
+Tree *rightLeftRotate(Tree *root) {
+ root->r = rightRotate(root->r);
+ return leftRotate(root);
+}
+
+// 插入节点
+Tree *insertNode(Tree *root, int val) {
+ if (root == NULL) {
+ Tree *tmp = (Tree *)malloc(sizeof(Tree));
+ tmp->val = val;
+ tmp->l = NULL;
+ tmp->r = NULL;
+ tmp->parent = NULL;
+ tmp->height = 1;
+ tmp->balance = 0;
+ return tmp;
+ }
+
+ if (val < root->val) {
+ root->l = insertNode(root->l, val);
+ root->l->parent = root;
+ } else {
+ root->r = insertNode(root->r, val);
+ root->r->parent = root;
+ }
+
+ updateHeight(root);
+ if (root->balance > 1) {
+ if (val < root->l->val) {
+ return rightRotate(root);
+ } else {
+ return leftRightRotate(root);
+ }
+ } else if (root->balance < -1) {
+ if (val > root->r->val) {
+ return leftRotate(root);
+ } else {
+ return rightLeftRotate(root);
+ }
+ }
+
+ return root;
+}
+
+// 删除节点
+Tree *deleteNode(Tree *root, int val) {
+ if (root == NULL)
+ return NULL;
+
+ if (val < root->val) {
+ root->l = deleteNode(root->l, val);
+ } else if (val > root->val) {
+ root->r = deleteNode(root->r, val);
+ } else {
+ if (root->l == NULL && root->r == NULL) {
+ free(root);
+ return NULL;
+ } else if (root->l == NULL) {
+ Tree *temp = root->r;
+ free(root);
+ return temp;
+ } else if (root->r == NULL) {
+ Tree *temp = root->l;
+ free(root);
+ return temp;
+ } else {
+ Tree *minNode = root->r;
+ while (minNode->l != NULL)
+ minNode = minNode->l;
+ root->val = minNode->val;
+ root->r = deleteNode(root->r, minNode->val);
+ }
+ }
+
+ updateHeight(root);
+ if (root->balance > 1) {
+ if (getHeight(root->l->l) >= getHeight(root->l->r)) {
+ return rightRotate(root);
+ } else {
+ return leftRightRotate(root);
+ }
+ } else if (root->balance < -1) {
+ if (getHeight(root->r->r) >= getHeight(root->r->l)) {
+ return leftRotate(root);
+ } else {
+ return rightLeftRotate(root);
+ }
+ }
+
+ return root;
+}
+
+void makeTree(Tree *root, int val) {
+ if (val < root->val) {
+ if (root->l == NULL) {
+ root->l = (Tree *)malloc(sizeof(Tree));
+ root->l->val = val;
+ root->l->l = NULL;
+ root->l->r = NULL;
+ root->l->parent = root;
+ root->l->height = root->height + 1;
+ } else {
+ makeTree(root->l, val);
+ }
+ } else {
+ if (root->r == NULL) {
+ root->r = (Tree *)malloc(sizeof(Tree));
+ root->r->val = val;
+ root->r->l = NULL;
+ root->r->r = NULL;
+ root->r->parent = root;
+ root->r->height = root->height + 1;
+
+ } else {
+ makeTree(root->r, val);
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+// 中序遍历
+void inOrder(Tree *root) {
+ if (root == NULL)
+ return;
+ inOrder(root->l);
+ printf("%d ", root->val);
+ inOrder(root->r);
+}
+
+// 二叉排序树T查找成功的平均查找长度
+double ASL(Tree *root, int level) {
+ if (root == NULL)
+ return 0;
+ return level + ASL(root->l, level + 1) + ASL(root->r, level + 1);
+}
+
+// 找到二叉树中值为val的节点并删除
+void delNode(Tree *root, int val) {
+ if (root == NULL)
+ return;
+ if (root->val == val) {
+ if (root->l == NULL && root->r == NULL) {
+ if (root->parent->l == root) {
+ root->parent->l = NULL;
+ } else {
+ root->parent->r = NULL;
+ }
+ free(root);
+ } else if (root->l == NULL) {
+ if (root->parent->l == root) {
+ root->parent->l = root->r;
+ } else {
+ root->parent->r = root->r;
+ }
+ free(root);
+ } else if (root->r == NULL) {
+ if (root->parent->l == root) {
+ root->parent->l = root->l;
+ } else {
+ root->parent->r = root->l;
+ }
+ free(root);
+ } else {
+ Tree *p = root->r;
+ while (p->l != NULL) {
+ p = p->l;
+ }
+ root->val = p->val;
+ delNode(p, p->val);
+ }
+ } else if (root->val > val) {
+ delNode(root->l, val);
+ } else {
+ delNode(root->r, val);
+ }
+}
+
+void detail(Tree *root) {
+ if (root == NULL)
+ return;
+ printf("val: %d, height: %d, balance: %d, parent: %d\n", root->val,
+ root->height, root->balance,
+ root->parent == NULL ? -1 : root->parent->val);
+ detail(root->l);
+ detail(root->r);
+}
+
+void pt(Tree *root) {
+ printf("inOrder:\n");
+ inOrder(root);
+ printf("\n");
+ detail(root);
+ printf("ASL: %lf\n", ASL(root, 1) / n);
+ printf("\n");
+}
+
+// 打印二叉树
+void printTree(Tree *root, int level) {
+ if (root == NULL)
+ return;
+ printTree(root->r, level + 1);
+ for (int i = 0; i < level; i++)
+ printf(" ");
+ printf("%d\n", root->val);
+ printTree(root->l, level + 1);
+}
+
+
+int main() {
+ freopen("data.in", "r", stdin);
+ scanf("%d", &n);
+ Tree *root = NULL;
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ int val;
+ scanf("%d", &val);
+ root = insertNode(root, val);
+ }
+ pt(root);
+
+ scanf("%d", &m);
+ for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
+ int x;
+ scanf("%d", &x);
+ root = deleteNode(root, x);
+ pt(root);
+ printTree(root, 0);
+ printf("----------------\n");
+ }
+
+ return 0;
+}
+10
+2 5 10 8 7 9 4 6 1 3
+3
+2
+5
+9
+二叉树图形输出为竖着
+1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
+val: 5, height: 4, balance: 0, parent: -1
+val: 2, height: 3, balance: -1, parent: 5
+val: 1, height: 1, balance: 0, parent: 2
+val: 4, height: 2, balance: 1, parent: 2
+val: 3, height: 1, balance: 0, parent: 4
+val: 8, height: 3, balance: 0, parent: 5
+val: 7, height: 2, balance: 1, parent: 8
+val: 6, height: 1, balance: 0, parent: 7
+val: 10, height: 2, balance: 1, parent: 8
+val: 9, height: 1, balance: 0, parent: 10
+ASL: 2.900000
+
+inOrder:
+1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
+val: 5, height: 4, balance: -1, parent: -1
+val: 3, height: 2, balance: 0, parent: 5
+val: 1, height: 1, balance: 0, parent: 3
+val: 4, height: 1, balance: 0, parent: 3
+val: 8, height: 3, balance: 0, parent: 5
+val: 7, height: 2, balance: 1, parent: 8
+val: 6, height: 1, balance: 0, parent: 7
+val: 10, height: 2, balance: 1, parent: 8
+val: 9, height: 1, balance: 0, parent: 10
+ASL: 2.500000
+
+ 10
+ 9
+ 8
+ 7
+ 6
+5
+ 4
+ 3
+ 1
+----------------
+inOrder:
+1 3 4 6 7 8 9 10
+val: 6, height: 4, balance: -1, parent: -1
+val: 3, height: 2, balance: 0, parent: 6
+val: 1, height: 1, balance: 0, parent: 3
+val: 4, height: 1, balance: 0, parent: 3
+val: 8, height: 3, balance: -1, parent: 6
+val: 7, height: 1, balance: 0, parent: 8
+val: 10, height: 2, balance: 1, parent: 8
+val: 9, height: 1, balance: 0, parent: 10
+ASL: 2.100000
+
+ 10
+ 9
+ 8
+ 7
+6
+ 4
+ 3
+ 1
+----------------
+inOrder:
+1 3 4 6 7 8 10
+val: 6, height: 3, balance: 0, parent: -1
+val: 3, height: 2, balance: 0, parent: 6
+val: 1, height: 1, balance: 0, parent: 3
+val: 4, height: 1, balance: 0, parent: 3
+val: 8, height: 2, balance: 0, parent: 6
+val: 7, height: 1, balance: 0, parent: 8
+val: 10, height: 1, balance: 0, parent: 8
+ASL: 1.700000
+
+ 10
+ 8
+ 7
+6
+ 4
+ 3
+ 1
+----------------
+录入、保存一个班级学生多门课程的成绩,并对成绩进行分析。
+input.dat。input.dat 中的数据进行处理,要求具有如下功能:
+60-69分人数、70-79分人数、 80-89分人数、90分以上人数。#include <stdio.h>
+#include <stdlib.h>
+#include <string.h>
+
+typedef struct {
+ char *uid;
+ char *name;
+ int math, eng, cs;
+} Score;
+
+// 保存到文件
+void save_to_file(Score **scores, int n, char *file_name) {
+ FILE *fp = fopen(file_name, "w");
+ fprintf(fp, "%d\n", n);
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ fprintf(fp, "%s %s %d %d %d\n", scores[i]->uid, scores[i]->name,
+ scores[i]->math, scores[i]->eng, scores[i]->cs);
+ }
+ fclose(fp);
+}
+
+int main() {
+ Score *scores[105];
+ int n;
+ // 如果 score.dat 不存在,就从键盘输入
+ FILE *fp = fopen("score.dat", "r");
+ if (fp == NULL) {
+ printf("score.dat not found, please input:\n");
+ scanf("%d", &n);
+ fp = fopen("score.dat", "w");
+ fprintf(fp, "%d\n", n);
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ scores[i] = (Score *)malloc(sizeof(Score));
+ char *uid = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * 105);
+ char *name = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * 105);
+ scanf("%s %s %d %d %d", uid, name, &scores[i]->math,
+ &scores[i]->eng, &scores[i]->cs);
+ scores[i]->uid = uid;
+ scores[i]->name = name;
+ fprintf(fp, "%s %s %d %d %d\n", scores[i]->uid, scores[i]->name,
+ scores[i]->math, scores[i]->eng, scores[i]->cs);
+ }
+ fclose(fp);
+ } else {
+ // 从 score.dat 读取
+ fscanf(fp, "%d", &n);
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ scores[i] = (Score *)malloc(sizeof(Score));
+ char *uid = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * 105);
+ char *name = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * 105);
+ fscanf(fp, "%s %s %d %d %d", uid, name, &scores[i]->math,
+ &scores[i]->eng, &scores[i]->cs);
+ scores[i]->uid = uid;
+ scores[i]->name = name;
+ }
+ fclose(fp);
+ }
+
+ printf("Total: %d\n", n);
+
+ printf("当前数据:\n");
+ // 输出所有人的信息
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ printf("%s %s %d %d %d\n", scores[i]->uid, scores[i]->name,
+ scores[i]->math, scores[i]->eng, scores[i]->cs);
+ }
+ printf("--------------------\n");
+
+ // 按照每个科目排序并输出对应的排名
+ printf("按照数学成绩排序:\n");
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ int max = i;
+ for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
+ if (scores[j]->math > scores[max]->math) {
+ max = j;
+ }
+ }
+ Score *tmp = scores[i];
+ scores[i] = scores[max];
+ scores[max] = tmp;
+ printf("%s %s %d %d %d\n", scores[i]->uid, scores[i]->name,
+ scores[i]->math, scores[i]->eng, scores[i]->cs);
+ }
+ save_to_file(scores, n, "math.dat");
+ printf("--------------------\n");
+
+ printf("按照英语成绩排序:\n");
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ int max = i;
+ for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
+ if (scores[j]->eng > scores[max]->eng) {
+ max = j;
+ }
+ }
+ Score *tmp = scores[i];
+ scores[i] = scores[max];
+ scores[max] = tmp;
+ printf("%s %s %d %d %d\n", scores[i]->uid, scores[i]->name,
+ scores[i]->math, scores[i]->eng, scores[i]->cs);
+ }
+ save_to_file(scores, n, "eng.dat");
+ printf("--------------------\n");
+
+ printf("按照计算机成绩排序:\n");
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ int max = i;
+ for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
+ if (scores[j]->cs > scores[max]->cs) {
+ max = j;
+ }
+ }
+ Score *tmp = scores[i];
+ scores[i] = scores[max];
+ scores[max] = tmp;
+ printf("%s %s %d %d %d\n", scores[i]->uid, scores[i]->name,
+ scores[i]->math, scores[i]->eng, scores[i]->cs);
+ }
+ save_to_file(scores, n, "cs.dat");
+ printf("--------------------\n");
+
+ // 计算平均分,按平均成绩排序,写到 average.dat
+ printf("平均分:\n");
+ FILE *fp_average = fopen("average.dat", "w");
+ fprintf(fp_average, "%d\n", n);
+ double avg_scores[105];
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ avg_scores[i] =
+ (scores[i]->math + scores[i]->eng + scores[i]->cs) / 3.0;
+ }
+ // sort
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ int max = i;
+ for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
+ if (avg_scores[j] > avg_scores[max]) {
+ max = j;
+ }
+ }
+ int tmp = avg_scores[i];
+ avg_scores[i] = avg_scores[max];
+ avg_scores[max] = tmp;
+ Score *tmp_score = scores[i];
+ scores[i] = scores[max];
+ scores[max] = tmp_score;
+ }
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ printf("%s %s %d %d %d %.2f\n", scores[i]->uid, scores[i]->name,
+ scores[i]->math, scores[i]->eng, scores[i]->cs,
+ avg_scores[i] * 1.0);
+ fprintf(fp_average, "%s %s %d %d %d %.2f\n", scores[i]->uid,
+ scores[i]->name, scores[i]->math, scores[i]->eng, scores[i]->cs,
+ avg_scores[i] * 1.0);
+ }
+ fclose(fp_average);
+ printf("--------------------\n");
+
+ // 求出各门课程的平均成绩、最高分、最低分、不及格人数、60-69分人数、70-79分人数、
+ // 80-89分人数、90分以上人数。
+ int math_sum = 0, eng_sum = 0, cs_sum = 0;
+ int math_max = 0, eng_max = 0, cs_max = 0;
+ int math_min = 100, eng_min = 100, cs_min = 100;
+ int math_fail = 0, eng_fail = 0, cs_fail = 0;
+ int math_60_69 = 0, eng_60_69 = 0, cs_60_69 = 0;
+ int math_70_79 = 0, eng_70_79 = 0, cs_70_79 = 0;
+ int math_80_89 = 0, eng_80_89 = 0, cs_80_89 = 0;
+ int math_90 = 0, eng_90 = 0, cs_90 = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ math_sum += scores[i]->math;
+ eng_sum += scores[i]->eng;
+ cs_sum += scores[i]->cs;
+ if (scores[i]->math > math_max) {
+ math_max = scores[i]->math;
+ }
+ if (scores[i]->eng > eng_max) {
+ eng_max = scores[i]->eng;
+ }
+ if (scores[i]->cs > cs_max) {
+ cs_max = scores[i]->cs;
+ }
+ if (scores[i]->math < math_min) {
+ math_min = scores[i]->math;
+ }
+ if (scores[i]->eng < eng_min) {
+ eng_min = scores[i]->eng;
+ }
+ if (scores[i]->cs < cs_min) {
+ cs_min = scores[i]->cs;
+ }
+ if (scores[i]->math < 60) {
+ math_fail++;
+ }
+ if (scores[i]->eng < 60) {
+ eng_fail++;
+ }
+ if (scores[i]->cs < 60) {
+ cs_fail++;
+ }
+ if (scores[i]->math >= 60 && scores[i]->math <= 69) {
+ math_60_69++;
+ }
+ if (scores[i]->eng >= 60 && scores[i]->eng <= 69) {
+ eng_60_69++;
+ }
+ if (scores[i]->cs >= 60 && scores[i]->cs <= 69) {
+ cs_60_69++;
+ }
+ if (scores[i]->math >= 70 && scores[i]->math <= 79) {
+ math_70_79++;
+ }
+ if (scores[i]->eng >= 70 && scores[i]->eng <= 79) {
+ eng_70_79++;
+ }
+ if (scores[i]->cs >= 70 && scores[i]->cs <= 79) {
+ cs_70_79++;
+ }
+ if (scores[i]->math >= 80 && scores[i]->math <= 89) {
+ math_80_89++;
+ }
+ if (scores[i]->eng >= 80 && scores[i]->eng <= 89) {
+ eng_80_89++;
+ }
+ if (scores[i]->cs >= 80 && scores[i]->cs <= 89) {
+ cs_80_89++;
+ }
+ if (scores[i]->math >= 90) {
+ math_90++;
+ }
+ if (scores[i]->eng >= 90) {
+ eng_90++;
+ }
+ if (scores[i]->cs >= 90) {
+ cs_90++;
+ }
+ }
+ printf("数学:\n平均分:%.2f 最高分:%d 最低分:%d 不及格人数:%d "
+ "60-69分人数:%d "
+ "70-79分人数:%d 80-89分人数:%d 90分以上人数:%d\n",
+ math_sum * 1.0 / n, math_max, math_min, math_fail, math_60_69,
+ math_70_79, math_80_89, math_90);
+ printf("英语:\n平均分:%.2f 最高分:%d 最低分:%d 不及格人数:%d "
+ "60-69分人数:%d "
+ "70-79分人数:%d 80-89分人数:%d 90分以上人数:%d\n",
+ eng_sum * 1.0 / n, eng_max, eng_min, eng_fail, eng_60_69, eng_70_79,
+ eng_80_89, eng_90);
+ printf("计算机:\n平均分:%.2f 最高分:%d 最低分:%d 不及格人数:%d "
+ "60-69分人数:%d "
+ "70-79分人数:%d 80-89分人数:%d 90分以上人数:%d\n",
+ cs_sum * 1.0 / n, cs_max, cs_min, cs_fail, cs_60_69, cs_70_79,
+ cs_80_89, cs_90);
+
+ // 根据姓名或学号查询某人的各门成绩,重名情况也能处理。
+ while (1) {
+ printf("请输入学号或姓名:\n");
+ char *query = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * 105);
+ scanf("%s", query);
+ int found = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ if (strcmp(scores[i]->uid, query) == 0 ||
+ strcmp(scores[i]->name, query) == 0) {
+ printf("%s %s %d %d %d\n", scores[i]->uid, scores[i]->name,
+ scores[i]->math, scores[i]->eng, scores[i]->cs);
+ found = 1;
+ }
+ }
+ if (!found) {
+ printf("未找到\n");
+ }
+ }
+ return 0;
+}
+7
+001 L1 78 77 90
+002 L2 89 67 88
+003 L3 56 66 78
+004 L4 89 86 85
+005 L5 67 88 76
+006 L6 45 54 67
+007 L6 78 76 70
+Total: 7
+当前数据:
+001 L1 78 77 90
+002 L2 89 67 88
+003 L3 56 66 78
+004 L4 89 86 85
+005 L5 67 88 76
+006 L6 45 54 67
+007 L6 78 76 70
+--------------------
+按照数学成绩排序:
+002 L2 89 67 88
+004 L4 89 86 85
+001 L1 78 77 90
+007 L6 78 76 70
+005 L5 67 88 76
+003 L3 56 66 78
+006 L6 45 54 67
+--------------------
+按照英语成绩排序:
+005 L5 67 88 76
+004 L4 89 86 85
+001 L1 78 77 90
+007 L6 78 76 70
+002 L2 89 67 88
+003 L3 56 66 78
+006 L6 45 54 67
+--------------------
+按照计算机成绩排序:
+001 L1 78 77 90
+002 L2 89 67 88
+004 L4 89 86 85
+003 L3 56 66 78
+005 L5 67 88 76
+007 L6 78 76 70
+006 L6 45 54 67
+--------------------
+平均分:
+004 L4 89 86 85 86.67
+002 L2 89 67 88 81.00
+001 L1 78 77 90 81.00
+005 L5 67 88 76 77.00
+007 L6 78 76 70 74.67
+003 L3 56 66 78 66.00
+006 L6 45 54 67 55.00
+--------------------
+数学:
+平均分:71.71 最高分:89 最低分:45 不及格人数:2 60-69分人数:1 70-79分人数:2 80-89分人数:2 90分以上人数:0
+英语:
+平均分:73.43 最高分:88 最低分:54 不及格人数:1 60-69分人数:2 70-79分人数:2 80-89分人数:2 90分以上人数:0
+计算机:
+平均分:79.14 最高分:90 最低分:67 不及格人数:0 60-69分人数:1 70-79分人数:3 80-89分人数:2 90分以上人数:1
+请输入学号或姓名:
+L1
+001 L1 78 77 90
+请输入学号或姓名:
+L2
+002 L2 89 67 88
+请输入学号或姓名:
+L6
+007 L6 78 76 70
+006 L6 45 54 67
+> EOF <
+这是一个一元稀疏多项式的简单计算器,需要设计一种数据结构来存储多项式,并实现多项式的输入、输出、加法、减法和计算多项式在某个点的值的功能。
+采用带表头结点的单链表来存储多项式。链表的每个节点表示多项式的一项,节点包含两个成员变量:系数和指数。
+x的指数次方,并累加到结果中。直接模拟
+#include <math.h>
+#include <stdio.h>
+#include <stdlib.h>
+
+typedef struct Node {
+ int c, e;
+ struct Node *next;
+} Node;
+
+typedef struct List {
+ Node head;
+ int len;
+} List;
+
+// 初始化链表
+List *init_list() {
+ List *l = (List *)malloc(sizeof(List));
+ l->head.next = NULL;
+ l->len = 0;
+ return l;
+}
+
+// 降序插入
+void insert(List *l, int c, int e) {
+ Node *p = &(l->head);
+ while (p->next && p->next->e > e) {
+ p = p->next;
+ }
+ if (p->next && p->next->e == e) {
+ p->next->c += c;
+ if (p->next->c == 0) {
+ Node *q = p->next;
+ p->next = q->next;
+ free(q);
+ l->len--;
+ }
+ } else {
+ Node *q = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
+ q->c = c, q->e = e;
+ q->next = p->next;
+ p->next = q;
+ l->len++;
+ }
+}
+
+// 只输出
+void output(List *l) {
+ Node *p = l->head.next;
+ printf("%d,", l->len);
+ while (p) {
+ printf("%d,%d", p->c, p->e);
+ p = p->next;
+ if (p)
+ printf(",");
+ }
+ printf("\n");
+}
+
+// 只输出
+void plus(List *l1, List *l2) {
+ Node *p1 = l1->head.next, *p2 = l2->head.next;
+ while (p1 && p2) {
+ if (p1->e > p2->e) {
+ printf("%d,%d,", p1->c, p1->e);
+ p1 = p1->next;
+ } else if (p1->e < p2->e) {
+ printf("%d,%d,", p2->c, p2->e);
+ p2 = p2->next;
+ } else {
+ printf("%d,%d,", p1->c + p2->c, p1->e);
+ p1 = p1->next;
+ p2 = p2->next;
+ }
+ }
+ while (p1) {
+ printf("%d,%d,", p1->c, p1->e);
+ p1 = p1->next;
+ }
+ while (p2) {
+ printf("%d,%d,", p2->c, p2->e);
+ p2 = p2->next;
+ }
+ printf("\n");
+}
+
+// 只输出
+void minus(List *l1, List *l2) {
+ Node *p1 = l1->head.next, *p2 = l2->head.next;
+ while (p1 && p2) {
+ if (p1->e > p2->e) {
+ printf("%d,%d,", p1->c, p1->e);
+ p1 = p1->next;
+ } else if (p1->e < p2->e) {
+ printf("%d,%d,", -p2->c, p2->e);
+ p2 = p2->next;
+ } else {
+ printf("%d,%d,", p1->c - p2->c, p1->e);
+ p1 = p1->next;
+ p2 = p2->next;
+ }
+ }
+ while (p1) {
+ printf("%d,%d,", p1->c, p1->e);
+ p1 = p1->next;
+ }
+ while (p2) {
+ printf("%d,%d,", -p2->c, p2->e);
+ p2 = p2->next;
+ }
+ printf("\n");
+}
+
+int calc(List *l, int x) {
+ int sum = 0;
+ Node *p = l->head.next;
+ while (p) {
+ sum += p->c * pow(x, p->e);
+ p = p->next;
+ }
+ return sum;
+}
+
+int main() {
+ // freopen("data.in", "r", stdin);
+ List *l = init_list();
+ List *l2 = init_list();
+ int n1, n2, c, e;
+ scanf("%d", &n1);
+ for (int i = 0; i < n1; i++) {
+ scanf("%d%d", &c, &e);
+ insert(l, c, e);
+ }
+ scanf("%d", &n2);
+ for (int i = 0; i < n2; i++) {
+ scanf("%d%d", &c, &e);
+ insert(l2, c, e);
+ }
+ output(l);
+ output(l2);
+ plus(l, l2);
+ minus(l, l2);
+ while (1) {
+ printf("请输入x的值:");
+ scanf("%d", &c);
+ if (c == -1)
+ break;
+ printf("%d\n", calc(l, c));
+ }
+ return 0;
+}
+4
+1 2
+5 2
+3 4
+666 9
+2
+1 3
+2 4
+3,666,9,3,4,6,2
+2,2,4,1,3
+666,9,5,4,1,3,6,2,
+666,9,1,4,-1,3,6,2,
+请输入x的值:1
+675
+请输入x的值:2
+341064
+请输入x的值:3
+13109175
+迷宫实验是取自心理学的一个古典实验。在该实验中,把一只老鼠从一个无顶大盒子的门放入,在盒中设置了许多墙,对行进方向形成了多处阻挡。盒子仅有一个出口,在出口处放置一块奶酪,吸引老鼠在迷宫中寻找道路以到达出口。对同一只老鼠重复进行上述实验,一直到老鼠从入口到出口,而不走错一步。老鼠经多次试验终于得到它学习走迷宫的路线。
+迷宫由m行n列的二维数组设置,0表示无障碍,1表示有障碍。设入口为(1,1),出口为(m,n),每次只能从一个无障碍单元移到周围四个方向上任一无障碍单元。编程实现对任意设定的迷宫,求出一条从入口到出口的通路,或得出没有通路的结论。 +算法输入:代表迷宫入口的坐标 +算法输出:穿过迷宫的结果。 算法要点:创建迷宫,试探法查找路。
+#include <stdio.h>
+#include <stdlib.h>
+#include <string.h>
+
+int m, n;
+int maze[105][105];
+
+// 存储当前路径
+char *path[10005];
+int path_len = 0;
+
+void dfs(int x, int y) {
+ if (x == m && y == n) {
+ // 找到出口
+ for (int i = 0; i < path_len; i++) {
+ printf("%s", path[i]);
+ if (i != path_len - 1) {
+ printf("->");
+ }
+ }
+ printf("\n");
+ return;
+ }
+ maze[x][y] = 1;
+ // 四个方向依次尝试
+ if (x + 1 <= m && maze[x + 1][y] == 0) {
+ path[path_len] = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * 105);
+ sprintf(path[path_len++], "(%d, %d)", x + 1, y);
+ dfs(x + 1, y);
+ path_len--;
+ }
+ if (y + 1 <= n && maze[x][y + 1] == 0) {
+ path[path_len] = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * 105);
+ sprintf(path[path_len++], "(%d, %d)", x, y + 1);
+ dfs(x, y + 1);
+ path_len--;
+ }
+ if (x - 1 >= 1 && maze[x - 1][y] == 0) {
+ path[path_len] = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * 105);
+ sprintf(path[path_len++], "(%d, %d)", x - 1, y);
+ dfs(x - 1, y);
+ path_len--;
+ }
+ if (y - 1 >= 1 && maze[x][y - 1] == 0) {
+ path[path_len] = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * 105);
+ sprintf(path[path_len++], "(%d, %d)", x, y - 1);
+ dfs(x, y - 1);
+ path_len--;
+ }
+}
+
+int main() {
+ freopen("data.in", "r", stdin);
+ scanf("%d%d", &m, &n);
+ for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
+ for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
+ scanf("%d", &maze[i][j]);
+ }
+ }
+ path[path_len] = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * 105);
+ strcpy(path[path_len++], "(1, 1)");
+ dfs(1, 1);
+
+ return 0;
+}
+7 6
+0 0 1 1 0 0
+1 0 0 0 0 0
+1 0 0 0 0 1
+1 0 0 0 0 1
+1 1 0 0 0 0
+1 1 1 1 0 0
+(1, 1)->(1, 2)->(2, 2)->(3, 2)->(4, 2)->(4, 3)->(5, 3)->(5, 4)->(5, 5)->(6, 5)->(7, 5)->(7, 6)
+(1, 1)->(1, 2)->(2, 2)->(3, 2)->(4, 2)->(4, 3)->(5, 3)->(5, 4)->(5, 5)->(6, 5)->(6, 6)->(7, 6)
+通过本学期的数据结构实验, 我对数据结构有了更深的理解, 也对C语言有了更深的理解. 通过实验, 我学会了如何使用C和C++语言来实现各种数据结构, 也学会了如何使用各种数据结构来解决实际问题.
Qt 版本的电子表格等待制作中, 预计在假期尝试.
Luthics 的个人博客:https://www.luthics.com/